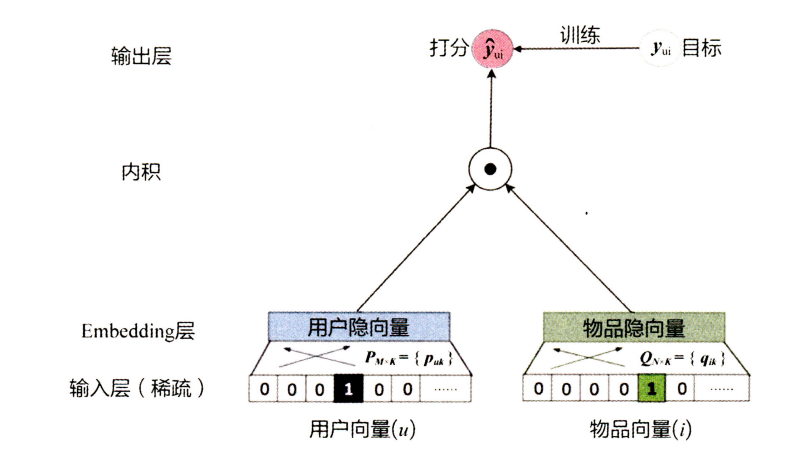
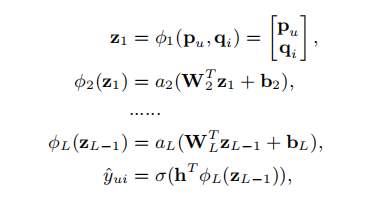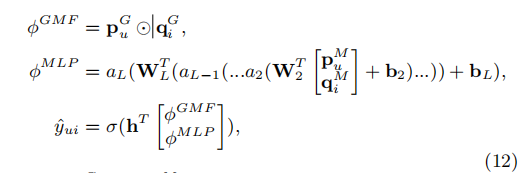本文主要参考了NeuralCf的论文,及王喆的《深度学习与推荐系统》一书,文中的图片也都来自于此。NeuralCF论文中文翻译
MF将用户和物品映射到相同的潜在空间中,因此可以用内积衡量两个用户之间的相似性,也可以等效为他们潜在向量之间的夹角的余弦。
使用Jaccard系数作为相似性系数
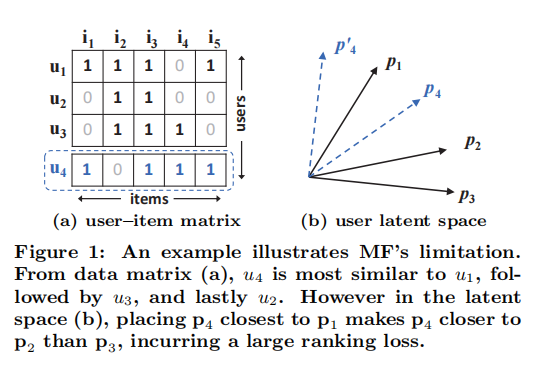
首先,我们关注图(a)的前三行用户,很容易得到s 23 ( 0.66 ) > s 12 ( 0.5 ) > s 13 ( 0.4 ) s_{23}(0.66)>s_{12}(0.5)>s_{13}(0.4) s 23 ( 0.66 ) > s 12 ( 0.5 ) > s 13 ( 0.4 ) p 1 , p 2 , p 3 p_{1},p_{2},p_{3} p 1 , p 2 , p 3 u 4 u_{4} u 4 s 41 ( 0.6 ) > s 43 ( 0.4 ) > s 42 ( 0.2 ) s_{41}(0.6) > s_{43}(0.4) > s_{42}(0.2) s 41 ( 0.6 ) > s 43 ( 0.4 ) > s 42 ( 0.2 ) u 4 u_{4} u 4 u 1 u_{1} u 1 u 3 u_{3} u 3 u 2 u_{2} u 2
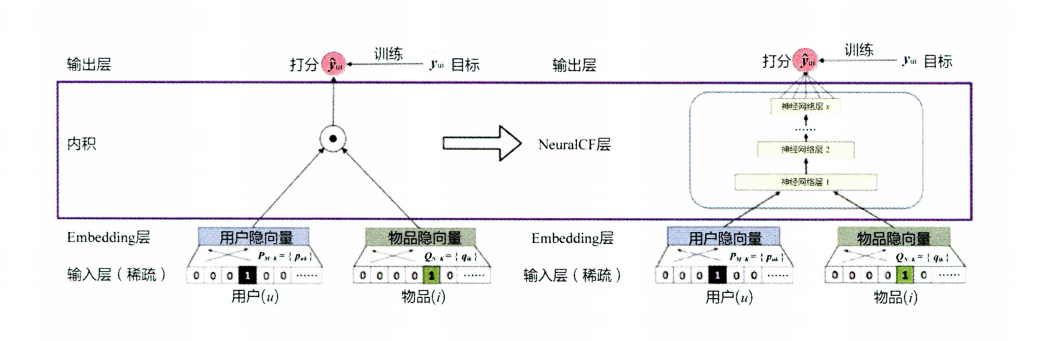
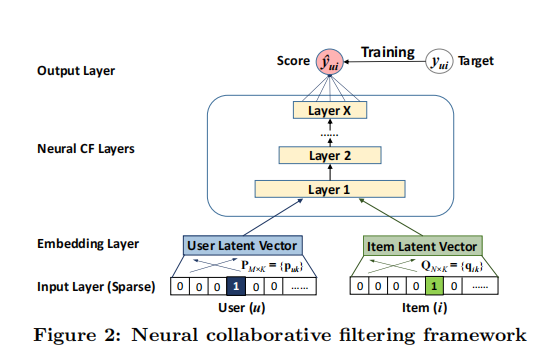
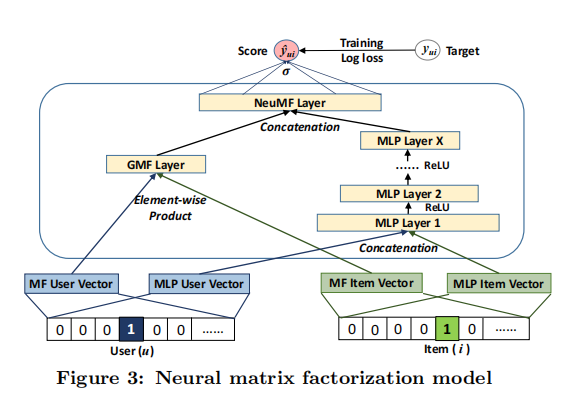
NCF模型
通用框架
y u i y_{ui} y u i v u U v_{u}^{U} v u U v i I v_{i}^{I} v i I y u i y_{ui} y u i y ^ u i {\hat{y}}_{ui} y ^ u i y u i y_{ui} y u i
y ^ u i = f ( P T v u U , Q T v i I ∣ P , Q , Θ f ) {\hat{y}}_{ui}=f(P^{T}v_{u}^{U},Q^{T}v_{i}^{I}| P,Q,\Theta _{f})
y ^ u i = f ( P T v u U , Q T v i I ∣ P , Q , Θ f )
这里的P ∈ R M ∗ K , Q ∈ R N ∗ K P \in R^{M*K},Q \in R^{N*K} P ∈ R M ∗ K , Q ∈ R N ∗ K Θ f \Theta_{f} Θ f
f ( P T v u U , Q T v i I ) = ϕ o u t ( ϕ X ( . . . ϕ 2 ( ϕ 1 ( P T v u U , Q T v i I ) ) . . . ) ) f(P^{T}v_{u}^{U},Q^{T}v_{i}^{I})=\phi_{out}(\phi_{X}(...\phi_{2}(\phi_{1}(P^{T}v_{u}^{U},Q^{T}v_{i}^{I}))...))
f ( P T v u U , Q T v i I ) = ϕ o u t ( ϕ X ( ... ϕ 2 ( ϕ 1 ( P T v u U , Q T v i I )) ... ))
ϕ o u t , ϕ x \phi_{out},\phi_{x} ϕ o u t , ϕ x
MCF的学习
为了学习模型参数,现有的pointwise方法大多使用了平方损失的回归:
L s q r = ∑ ( u , i ) ∈ y ∪ y − w u i ( y u i − y u i ^ ) 2 L_{sqr}=\sum_{(u,i)\in y ∪y-}w_{ui}(y_{ui}-{\hat{y_{ui}}})^{2}
L s q r = ( u , i ) ∈ y ∪ y − ∑ w u i ( y u i − y u i ^ ) 2
y表示了在Y中观察到的相互作用的集合,y-表示负向实例的集合。w u i w_{ui} w u i y u i y_{ui} y u i
考虑到隐式反馈的一类性质,我们可以将 y u i y_{ui} y u i y ^ u i {\hat{y}}_{ui} y ^ u i y ^ u i {\hat{y}}_{ui} y ^ u i ϕ o u t \phi_{out} ϕ o u t
p ( y , y − ∣ P , Q , Θ f ) = ∏ ( u , i ) ∈ y y ^ u i ∏ ( u , i ) ∈ y − ( 1 − y ^ u i ) p(y,y-|P,Q,\Theta_{f})=\prod_{(u,i)\in y}{\hat{y}}_{ui}\prod_{(u,i)\in y-}(1-{\hat{y}}_{ui})
p ( y , y − ∣ P , Q , Θ f ) = ( u , i ) ∈ y ∏ y ^ u i ( u , i ) ∈ y − ∏ ( 1 − y ^ u i )
取概率的负对数,我们得到:
L = − ∑ ( u , i ) ∈ y l o g y ^ u i − ∑ ( u , i ) ∈ y − l o g ( 1 − y ^ u i ) = − ∑ ( u , i ) ∈ y ⋃ y − ( y u i l o g y ^ u i + ( 1 − y u i ) l o g ( 1 − y ^ u i ) ) L=-\sum_{(u,i)\in y}log{\hat{y}}_{ui}-\sum_{(u,i)\in y-}log(1-{\hat{y}}_{ui})
=-\sum_{(u,i)\in y \bigcup y-}(y_{ui}log{\hat{y}}_{ui}+(1-y_{ui})log(1-{\hat{y}}_{ui})) L = − ( u , i ) ∈ y ∑ l o g y ^ u i − ( u , i ) ∈ y − ∑ l o g ( 1 − y ^ u i ) = − ( u , i ) ∈ y ⋃ y − ∑ ( y u i l o g y ^ u i + ( 1 − y u i ) l o g ( 1 − y ^ u i ))
这是NCF方法最小化的目标函数,其优化可以通过使用随机梯度下降(SGD)来实现。
这里的代价函数和我们熟悉的二分类交叉熵损失函数是一样的,通过对NCF的概率处理,我们将隐式反馈推荐作为一个二元分类问题。
广义矩阵分解(GMF)
p u p_{u} p u P T v u U P^{T}v_{u}^{U} P T v u U q i q_{i} q i Q T v v I Q^{T}v_{v}^{I} Q T v v I
ϕ 1 ( p u , q i ) = p u ⨀ q i \phi_{1}(p_{u},q_{i})=p_{u}\bigodot q_{i}
ϕ 1 ( p u , q i ) = p u ⨀ q i
⨀ \bigodot ⨀
y ^ u i = a o u t ( h T ( p u ⨀ q i ) ) {\hat{y}}_{ui}=a_{out}(h^{T}(p_{u}\bigodot q_{i}))
y ^ u i = a o u t ( h T ( p u ⨀ q i ))
a o u t a_{out} a o u t a o u t a_{out} a o u t a o u t a_{out} a o u t
多层感知机(MLP)
由于NCF采用两种路径来对用户和项目进行建模,所以将这两种路径的特征串联起来是很直观的。然而,简单的向量连接并不能解释用户和物品的潜在特征之间的任何交互,这对于协同过滤进行建模效果是不够的。为了解决这个问题,我们建议在连接的向量上添加隐藏层,使用一个标准的MLP来学习用户和物品潜在特征之间的交互。从这个意义上说,我们可以赋予模型很大程度的灵活性和非线性来学习 p u p_{u} p u q i q_{i} q i W x , b x , a x W_{x},b_{x},a_{x} W x , b x , a x
GML和MLP融合
GMF采用线性核函数对潜在特征交互进行建模,MLP采用非线性核函数从数据中学习交互函数。接下来的问题是:我们如何在NCF框架下融合GMF和MLP,使得它们可以相互增强,从而更好地对复杂的用户-物品矩阵迭代交互进行建模。p u G p_{u}^{G} p u G p u M p_{u}^{M} p u M q i G q_{i}^{G} q i G q i M q_{i}^{M} q i M
预训练
由于NeuMF目标函数的非凸性,基于梯度的优化方法只能找到局部最优解。初始化对深度学习模型的收敛性和性能起着重要的作用。由于NeuMF是一个集成GMF和MLP的模型,我们建议使用GMF和MLP的预训练模型初始化NeuMF。
h ← [ α h G M F ( 1 − α ) h M L P ] h \gets\begin{bmatrix}
\alpha h^{GMF} \\
(1-\alpha)h^{MLP}
\end{bmatrix} h ← [ α h GMF ( 1 − α ) h M L P ]
其中,h G M F h^ {GMF} h GMF h M L P h^ {MLP} h M L P
代码
数据处理
1 2 import scipy.sparse as spimport numpy as np
1 2 3 4 5 dataset = 'ml-1m' main_path = './Data/' train_rating = main_path + '{}.train.rating' .format (dataset) test_rating = main_path + '{}.test.rating' .format (dataset) test_negative = main_path + '{}.test.negative' .format (dataset)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def load_rating_file_as_list (filename ): ratingList = [] with open (filename, "r" ) as f: line = f.readline() while line is not None and line != "" : arr = line.split("\t" ) user, item = int (arr[0 ]), int (arr[1 ]) ratingList.append([user, item]) line = f.readline() return ratingList
1 testRatings=load_rating_file_as_list(test_rating)
6040
[0, 25]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def load_negative_file (filename ): negativeList = [] with open (filename, "r" ) as f: line = f.readline() while line is not None and line != "" : arr = line.split("\t" ) negatives = [] for x in arr[1 :]: negatives.append(int (x)) negativeList.append(negatives) line = f.readline() return negativeList
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def load_testdata (filename ): test_data = [] with open (filename, "r" ) as f: line = f.readline() while line is not None and line != "" : arr = line.split("\t" ) u=eval (arr[0 ])[0 ] test_data.append([u, eval (arr[0 ])[1 ]]) for x in arr[1 :]: test_data.append([u,int (x)]) line = f.readline() return test_data
1 2 3 4 test_data=load_testdata(filename=test_negative) print (len (test_data))print (test_data[0 ])print (len (test_data[0 ]))
604000
[0, 25]
2
1 np.save('./ProcessedDate/testdate.npy' ,np.array(test_data))
1 testNegatives=load_negative_file(test_negative)
1 2 3 print (len (testNegatives))print (len (testNegatives[0 ]))testNegatives[0 ]
6040
99
[1064,
174,
2791,
3373,
269,
2678,
1902,
3641,
1216,
...
58,
2551,
2333,
2688,
3703,
1300,
1924,
3118]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 def load_rating_file_as_matrix (filename ): """ Read .rating file and Return dok matrix. The first line of .rating file is: num_users\t num_items """ num_users, num_items = 0 , 0 with open (filename, "r" ) as f: line = f.readline() while line is not None and line != "" : arr = line.split("\t" ) u, i = int (arr[0 ]), int (arr[1 ]) num_users = max (num_users, u) num_items = max (num_items, i) line = f.readline() mat = sp.dok_matrix((num_users + 1 , num_items + 1 ), dtype=np.float32) with open (filename, "r" ) as f: line = f.readline() while line is not None and line != "" : arr = line.split("\t" ) user, item, rating = int (arr[0 ]), int (arr[1 ]), float (arr[2 ]) if rating > 0 : mat[user, item] = 1.0 line = f.readline() return mat
1 trainMatrix=load_rating_file_as_matrix(train_rating)
(6040, 3706)
<1x3706 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.float32'>'
with 52 stored elements in Dictionary Of Keys format>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import pandas as pdtrain_data=pd.read_csv(train_rating,sep='\t' ,header=None , names=['user' , 'item' ], usecols=[0 , 1 ], dtype={0 : np.int32, 1 : np.int32}) user_number=train_data['user' ].max ()+1 item_number=train_data['item' ].max ()+1 train_data=train_data.values.tolist() trainMatrix1=sp.dok_matrix((user_number,item_number),dtype=np.float32) for train in train_data: trainMatrix1[train[0 ],train[1 ]]=1.0
994169
1 2 train_data=pd.read_csv(train_rating,sep='\t' ,header=None , names=['user' , 'item' ], usecols=[0 , 1 ], dtype={0 : np.int32, 1 : np.int32})
1 2 index=train_data[(train_data.user==549 )&(train_data['item' ]==1543 )].index.tolist() train_data.loc[index,:]
1 2 train_datalist=train_data.values.tolist() train_datalist[:20 ]
[[0, 32],
[0, 34],
[0, 4],
[0, 35],
[0, 30],
[0, 29],
[0, 33],
[0, 40],
[0, 10],
[0, 16],
[0, 23],
[0, 28],
[0, 12],
[0, 8],
[0, 5],
[0, 20],
[0, 46],
[0, 15],
[0, 50],
[0, 49]]
1 np.save('./ProcessedDate/train_datalist.npy' ,np.array(train_datalist))
(6040, 3706)
<1x3706 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.float32'>'
with 52 stored elements in Dictionary Of Keys format>
1 2 3 4 np.save('./ProcessedDate/trainMatrix.npy' ,trainMatrix1) np.save('./ProcessedDate/testRatings.npy' ,np.array(testRatings)) np.save('./ProcessedDate/testNegatives.npy' ,np.array(testNegatives))
####导包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import datetimeimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdfrom collections import Counterimport heapqimport torchfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset, TensorDatasetimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fimport torch.optim as optimimport warningswarnings.filterwarnings('ignore' ) import torch.utils.data as datadevice = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" ) ```python topK = 10 num_factors = 8 num_negatives = 4 batch_size = 64 lr = 0.001 layers=[num_factors*2 ,64 ,32 ,16 ,8 ]
从文件中导入数据进行处理
导入数据
train=np.load(‘./ProcessedDate/trainMatrix.npy’,allow_pickle=True).tolist()
scipy.sparse._dok.dok_matrix
994169
1 train_data=train_datalist
1 2 3 type (train_data)print (len (train_data))train_data[0 ]
994169
[0, 32]
1 2 num_users, num_items = train.shape num_users
6040
将数据送入dataloader
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class CFData (data.Dataset): def __init__ (self, features, num_item, train_mat=None , num_ng=0 , is_training=None ): """features=train_data,num_item=item_num,train_mat,稀疏矩阵,num_ng,训练阶段默认为4,即采样4-1个负样本对应一个评分过的 数据。 """ super (CFData, self).__init__() """ Note that the labels are only useful when training, we thus add them in the ng_sample() function. """ self.features = features self.num_item = num_item self.train_mat = train_mat self.num_ng = num_ng self.is_training = is_training def ng_sample (self ): assert self.is_training, 'no need to sampling when testing' self.features_fill = [] for (u,i) in self.train_mat.keys(): self.features_fill.append([u,i,1 ]) for t in range (self.num_ng): j=np.random.randint(self.num_item) while (u,j) in self.train_mat: j=np.random.randint(self.num_item) self.features_fill.append([u,j,0 ]) def __len__ (self ): return self.num_ng * len (self.features) if \ self.is_training else len (self.features) def __getitem__ (self, idx ): features = self.features_fill if \ self.is_training else self.features user = features[idx][0 ] item_i = features[idx][1 ] if self.is_training: labels=features[idx][2 ] else : if idx%100 ==0 : labels=1 else : labels=0 return user, item_i, labels
1 2 3 train_dataset = CFData( train_data, num_item=num_items, train_mat=train, num_ng=4 , is_training=True ) train_loader=DataLoader(train_dataset,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 train_loader.dataset.ng_sample() for (x,y,z) in (train_loader): print (x,y,z) break print (x.shape)print (y.shape)print (z.shape)
tensor([2806, 4053, 1088, 2453, 4214, 4276, 300, 4193, 3642, 3311, 2461, 4470,
3328, 2811, 255, 797, 3568, 548, 3128, 4052, 769, 3161, 2430, 838,
2736, 3355, 328, 2241, 3257, 2615, 3475, 2888, 3223, 3155, 4203, 1946,
2241, 2800, 3310, 1424, 4678, 562, 4770, 3689, 3104, 1997, 711, 1316,
2628, 2963, 4747, 2244, 3765, 1469, 1028, 3390, 939, 4052, 1054, 1223,
3280, 1477, 186, 586]) tensor([ 334, 2581, 3629, 3139, 3470, 1796, 1147, 1446, 2966, 3677, 1369, 968,
3537, 417, 628, 455, 2118, 1850, 2436, 1830, 2225, 2774, 1351, 1606,
1596, 1859, 2455, 2854, 1495, 337, 3214, 675, 1284, 979, 449, 211,
616, 1061, 3352, 3418, 933, 2505, 3393, 496, 381, 520, 3445, 155,
1393, 2275, 2432, 2389, 3186, 2265, 2652, 2692, 2590, 231, 2934, 97,
1008, 3598, 2490, 2178]) tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0])
torch.Size([64])
torch.Size([64])
torch.Size([64])
定义模型
MLP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class MLP (nn.Module): def __init__ (self,num_users,num_items,factor_num=32 ,layers=[20 ,64 ,32 ,16 ],regs=[0 ,0 ] ): super (MLP,self).__init__() self.MF_Embedding_User=nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=num_users,embedding_dim=factor_num) self.MF_Embedding_Item=nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=num_items,embedding_dim=factor_num) self.dnn_network = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(layer[0 ], layer[1 ]) for layer in list (zip (layers[:-1 ], layers[1 :]))]) self.linear=nn.Linear(layers[-1 ],1 ) self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid() def forward (self,inputs ): inputs=inputs.long() MF_Embedding_User=self.MF_Embedding_User(inputs[:,0 ]) MF_Embedding_Item=self.MF_Embedding_Item(inputs[:,1 ]) x=torch.cat([MF_Embedding_User,MF_Embedding_Item],dim=-1 ) for linear in self.dnn_network: x=linear(x) x=F.relu(x) x=self.linear(x) predictions=self.sigmoid(x) predictions = predictions.squeeze(-1 ) predictions=predictions.float () return predictions
1 2 3 model=MLP(num_users=num_users,num_items=num_items,factor_num=num_factors,layers=layers) model.to(device=device)
MLP(
(MF_Embedding_User): Embedding(6040, 8)
(MF_Embedding_Item): Embedding(3706, 8)
(dnn_network): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=64, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=32, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=16, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=8, bias=True)
)
(linear): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=1, bias=True)
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
1 2 3 x=x.reshape((-1 ,1 )) y=y.reshape((-1 ,1 )) a=torch.cat((x,y),dim=-1 )
1 2 3 print (model(a))model(a)[0 ]
tensor([0.4523, 0.4545, 0.4527, 0.4530, 0.4540, 0.4600, 0.4537, 0.4567, 0.4529,
0.4557, 0.4526, 0.4551, 0.4532, 0.4532, 0.4549, 0.4571, 0.4519, 0.4547,
0.4545, 0.4538, 0.4538, 0.4548, 0.4574, 0.4529, 0.4519, 0.4539, 0.4534,
0.4551, 0.4523, 0.4524, 0.4547, 0.4527, 0.4564, 0.4514, 0.4603, 0.4538,
0.4542, 0.4539, 0.4532, 0.4548, 0.4549, 0.4527, 0.4529, 0.4532, 0.4569,
0.4534, 0.4536, 0.4524, 0.4545, 0.4561, 0.4527, 0.4539, 0.4546, 0.4542,
0.4562, 0.4547, 0.4533, 0.4521, 0.4555, 0.4517, 0.4553, 0.4518, 0.4521,
0.4526], grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
tensor(0.4523, grad_fn=<SelectBackward0>)
GMF
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class GMF (nn.Module): def __init__ (self,num_uers,num_items,factor_numbers=32 ): super (GMF,self).__init__() self.MF_Embedding_User=nn.Embedding(num_uers,embedding_dim=factor_numbers) self.MF_Embedding_Item=nn.Embedding(num_items,factor_numbers) self.linear=nn.Linear(factor_numbers,1 ) self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid() def forward (self,inputs ): inputs=inputs.long() MF_Embedding_User=self.MF_Embedding_User(inputs[:,0 ]) MF_Embedding_Item=self.MF_Embedding_Item(inputs[:,1 ]) predict_vec=torch.mul(MF_Embedding_User,MF_Embedding_Item) linear=self.linear(predict_vec) output=self.sigmoid(linear) output=output.squeeze(-1 ) return output
1 2 model=GMF(num_users,num_items,num_factors) model.to(device)
GMF(
(MF_Embedding_User): Embedding(6040, 8)
(MF_Embedding_Item): Embedding(3706, 8)
(linear): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=1, bias=True)
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
1 2 3 4 x=x.reshape((-1 ,1 )) y=y.reshape((-1 ,1 )) a=torch.cat((x,y),dim=-1 ) print (model(a))
tensor([0.3108, 0.3083, 0.6403, ..., 0.8549, 0.8039, 0.3121],
grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
NMF
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class NeuralMF (nn.Module): def __init__ (self,num_users,num_items,mf_dim,layers ): super (NeuralMF,self).__init__() self.MF_Embedding_User=nn.Embedding(num_users,mf_dim) self.MF_Embedding_Item=nn.Embedding(num_items,mf_dim) self.MLP_Embedding_User=nn.Embedding(num_users,layers[0 ] //2 ) self.MLP_Embedding_Item=nn.Embedding(num_items,layers[0 ]//2 ) self.dnn_network=nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(layer[0 ], layer[1 ]) for layer in list (zip (layers[:-1 ], layers[1 :]))]) self.linear=nn.Linear(layers[-1 ],mf_dim) self.linear2=nn.Linear(2 *mf_dim,1 ) self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid() def forward (self,inputs ): inputs=inputs.long() MF_Embedding_User=self.MF_Embedding_User(inputs[:,0 ]) MF_Embedding_Item=self.MF_Embedding_Item(inputs[:,1 ]) mf_vec=torch.mul(MF_Embedding_User,MF_Embedding_Item) MLP_Embedding_User=self.MLP_Embedding_User(inputs[:,0 ]) MLP_Embedding_Item=self.MLP_Embedding_Item(inputs[:,1 ]) x=torch.cat([MLP_Embedding_User,MLP_Embedding_Item],dim=-1 ) for linear in self.dnn_network: x=linear(x) x=F.relu(x) mlp_vec=self.linear(x) vector=torch.cat([mf_vec,mlp_vec],dim=-1 ) linear=self.linear2(vector) output=self.sigmoid(linear) output=output.squeeze(-1 ) return output
1 2 model=NeuralMF(num_users,num_items,num_factors,layers) model.to(device)
NeuralMF(
(MF_Embedding_User): Embedding(6040, 8)
(MF_Embedding_Item): Embedding(3706, 8)
(MLP_Embedding_User): Embedding(6040, 8)
(MLP_Embedding_Item): Embedding(3706, 8)
(dnn_network): ModuleList(
(0): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=64, bias=True)
(1): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=32, bias=True)
(2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=16, bias=True)
(3): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=8, bias=True)
)
(linear): Linear(in_features=8, out_features=8, bias=True)
(linear2): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1, bias=True)
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
tensor([0.5335, 0.6584, 0.6141, 0.5763, 0.4243, 0.5309, 0.5333, 0.4247, 0.5536,
0.5929, 0.5608, 0.5473, 0.5609, 0.5059, 0.5331, 0.5905, 0.5931, 0.5454,
0.4831, 0.5259, 0.5547, 0.5405, 0.5677, 0.6399, 0.5988, 0.5861, 0.5574,
0.5722, 0.5028, 0.7629, 0.5612, 0.6122, 0.4081, 0.6269, 0.5933, 0.6069,
0.6996, 0.6164, 0.5964, 0.5967, 0.6911, 0.5107, 0.5526, 0.5478, 0.5358,
0.5651, 0.4293, 0.4630, 0.4618, 0.5442, 0.5680, 0.5080, 0.5040, 0.5064,
0.5338, 0.5138, 0.5314, 0.4367, 0.7294, 0.4487, 0.5008, 0.6045, 0.5884,
0.4132], grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
定义评价指标
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 _model = None _testRatings = None _testNegatives = None _K = None def getHitRatio (ranklist, gtItem ): for item in ranklist: if item == gtItem: return 1 return 0 def getNDCG (ranklist, gtItem ): for i in range (len (ranklist)): item = ranklist[i] if item == gtItem: return np.log(2 ) / np.log(i+2 ) return 0 def eval_one_rating (idx ): rating = _testRatings[idx] items = _testNegatives[idx] u = rating[0 ] gtItem = rating[1 ] items.append(gtItem) map_item_score = {} users = np.full(len (items), u, dtype='int32' ) test_data = torch.tensor(np.vstack([users, np.array(items)]).T).to(device) predictions = _model(test_data) for i in range (len (items)): item = items[i] map_item_score[item] = predictions[i].data.cpu().numpy() items.pop() ranklist = heapq.nlargest(_K, map_item_score, key=lambda k: map_item_score[k]) hr = getHitRatio(ranklist, gtItem) ndcg = getNDCG(ranklist, gtItem) return hr, ndcg def evaluate_model (model, testRatings, testNegatives, K ): """ Evaluate the performance (Hit_Ratio, NDCG) of top-K recommendation Return: score of each test rating. """ global _model global _testRatings global _testNegatives global _K _model = model _testNegatives = testNegatives _testRatings = testRatings _K = K hits, ndcgs = [], [] for idx in range (len (_testRatings)): (hr, ndcg) = eval_one_rating(idx) hits.append(hr) ndcgs.append(ndcg) return hits, ndcgs
1 2 3 4 (hits, ndcgs) = evaluate_model(model, testRatings, testNegatives, topK) hr, ndcg = np.array(hits).mean(), np.array(ndcgs).mean() print ('Init: HR=%.4f, NDCG=%.4f' %(hr, ndcg))
Init: HR=0.1017, NDCG=0.0466
训练
定义优化器
1 2 3 loss_func = nn.BCELoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=lr)
训练模型
这里以其中一个模型为例,展示训练过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 import timebest_hr, best_ndcg, best_iter = hr, ndcg, -1 epochs = 20 log_step_freq = 10000 for epoch in range (epochs): model.train() loss_sum = 0.0 start_time=time.time() train_loader.dataset.ng_sample() step=0 for user,item,labels in train_loader: step+=1 user=user.to(device) item=item.to(device) labels=labels.to(device) model.zero_grad() user=user.reshape((-1 ,1 )) item=item.reshape((-1 ,1 )) features=torch.cat((user,item),dim=-1 ) predictions = model(features) predictions=predictions.to(torch.float32) labels=labels.to(torch.float32) loss = loss_func(predictions, labels) loss.backward() optimizer.step() loss_sum += loss.item() if step % log_step_freq == 0 : print (("[step = %d] loss: %.3f" ) % (step, loss_sum/step)) model.eval () (hits, ndcgs) = evaluate_model(model, testRatings, testNegatives, topK) hr, ndcg = np.array(hits).mean(), np.array(ndcgs).mean() elapsed_time=time.time()-start_time print ("The time elapse of epoch {:03d}" .format (epoch) + " is: " + time.strftime("%H: %M: %S" , time.gmtime(elapsed_time))) if hr > best_hr: best_hr, best_ndcg, best_iter = hr, ndcg, epoch torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'Pre_train/m1-1m_NeuralMF.pkl' ) info = (epoch, loss_sum/step, hr, ndcg) print (("\nEPOCH = %d, loss = %.3f, hr = %.3f, ndcg = %.3f" ) %info) print ('Finished Training...' )
[step = 10000] loss: 0.263
[step = 20000] loss: 0.263
[step = 30000] loss: 0.264
[step = 40000] loss: 0.264
[step = 50000] loss: 0.264
[step = 60000] loss: 0.264
The time elapse of epoch 000 is: 00: 02: 52
EPOCH = 0, loss = 0.264, hr = 0.557, ndcg = 0.315
[step = 10000] loss: 0.261
[step = 20000] loss: 0.262
[step = 30000] loss: 0.262
[step = 40000] loss: 0.263
[step = 50000] loss: 0.263
[step = 60000] loss: 0.263
The time elapse of epoch 001 is: 00: 02: 51
EPOCH = 1, loss = 0.263, hr = 0.552, ndcg = 0.313
[step = 10000] loss: 0.260
[step = 20000] loss: 0.261
[step = 30000] loss: 0.262
[step = 40000] loss: 0.262
[step = 50000] loss: 0.262
[step = 60000] loss: 0.262
The time elapse of epoch 002 is: 00: 02: 52
EPOCH = 2, loss = 0.263, hr = 0.550, ndcg = 0.314
[step = 10000] loss: 0.259
[step = 20000] loss: 0.260
[step = 30000] loss: 0.261
[step = 40000] loss: 0.261
[step = 50000] loss: 0.262
[step = 60000] loss: 0.262
The time elapse of epoch 003 is: 00: 02: 50
EPOCH = 3, loss = 0.262, hr = 0.533, ndcg = 0.303
[step = 10000] loss: 0.259
[step = 20000] loss: 0.259
[step = 30000] loss: 0.260
[step = 40000] loss: 0.260
[step = 50000] loss: 0.261
[step = 60000] loss: 0.261
The time elapse of epoch 004 is: 00: 02: 50
EPOCH = 4, loss = 0.261, hr = 0.528, ndcg = 0.302